Solenoid valves are electromechanical devices that are widely used in various industries. They are commonly used to precisely control the flow of liquids and gases through a pipe or a duct. Solenoid valves are highly reliable and can be operated remotely, making them popular in many applications. This post explains solenoid valves, their uses, functions, working principle, types, and how to control them.
What is a solenoid valve?
A solenoid valve is an electromechanical device that controls the flow of fluids and gases by using an electric current to create a magnetic field. It consists of a coil, plunger, spring, and valve body. The coil is wound around the plunger, which is magnetized when an electric current flows through it. The magnetic force moves the plunger, compresses the spring, and opens or closes the valve. The valve body is connected to the plunger and controls the flow of the liquid or gas through the pipe.
What is a solenoid valve used for?
Solenoid valves are used in a wide range of applications, including:
Water treatment plants:
Solenoid valves are used to control water flow through the pipes in water treatment plants.
Oil and gas industry:
Solenoid valves are used to control the flow of oil and gas through pipelines.
Medical equipment:
Solenoid valves are used in medical equipment such as blood analyzers, ventilators, and dialysis machines to control the flow of gases and liquids.
HVAC systems:
Solenoid valves are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to control refrigerant flow through the air conditioning and heating systems.
Industrial automation:
Solenoid valves are used in industrial automation systems to control the flow of fluids and gases in production lines. They are commonly preferred in industrial processes such as water treatment, food processing, and chemical production.
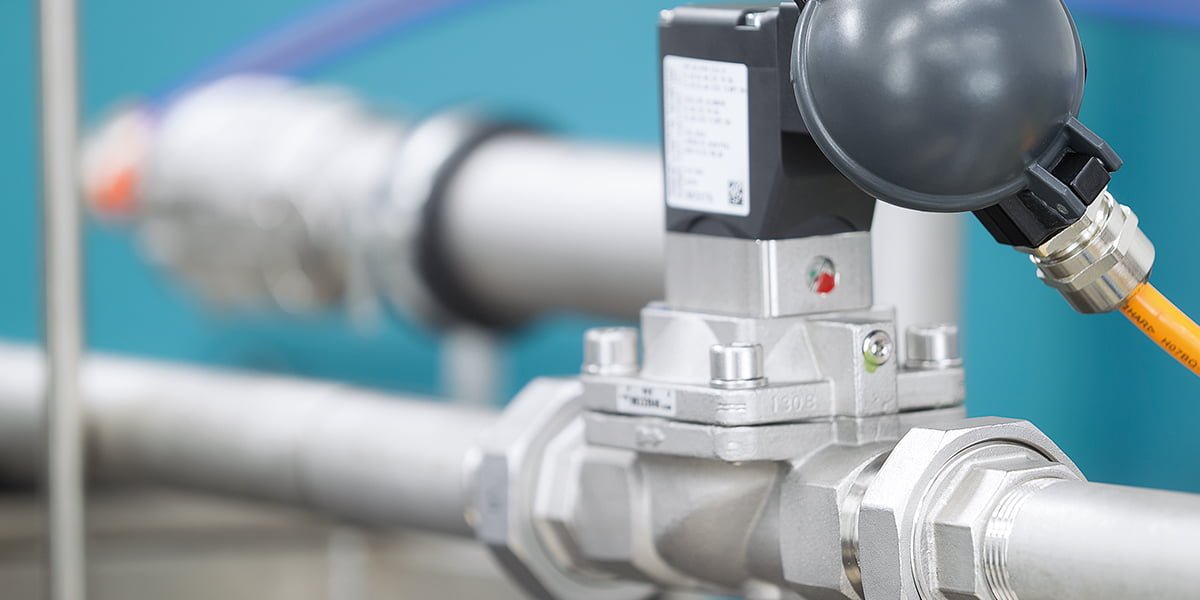

What are the functions of solenoid valves?
The main function of a solenoid valve is to control the flow of liquids and gases through a pipe or duct. Solenoid valves are designed to open or close quickly in response to an electric signal. They can be used to turn on or off the flow of fluids and gases, or they can be used to regulate the flow by adjusting the valve opening.
Functions of solenoid valves are:
Control: Solenoid valves control the flow of fluids and gases.
Isolation: Solenoid valves are used to isolate different parts of a system.
Safety: Solenoid valves are used to shut down a system in case of an emergency.
How does a solenoid valve work?
The solenoid valve works on the principle of electromagnetism. When an electric current is passed through the coil, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field attracts the plunger connected to the valve disc. The plunger moves against the spring force and opens the valve. The magnetic field disappears when the electric current is turned off, and the spring force closes the valve.
What is the working principle of solenoid valves?
The working principle of a solenoid valve is based on the interaction between an electromagnetic field and a mechanical valve. A magnetic field is generated when a current passes through the coil, which moves the plunger, and the valve opens. When the current is turned off, the magnetic field disappears. The spring force returns the plunger to its original position, closing the valve.
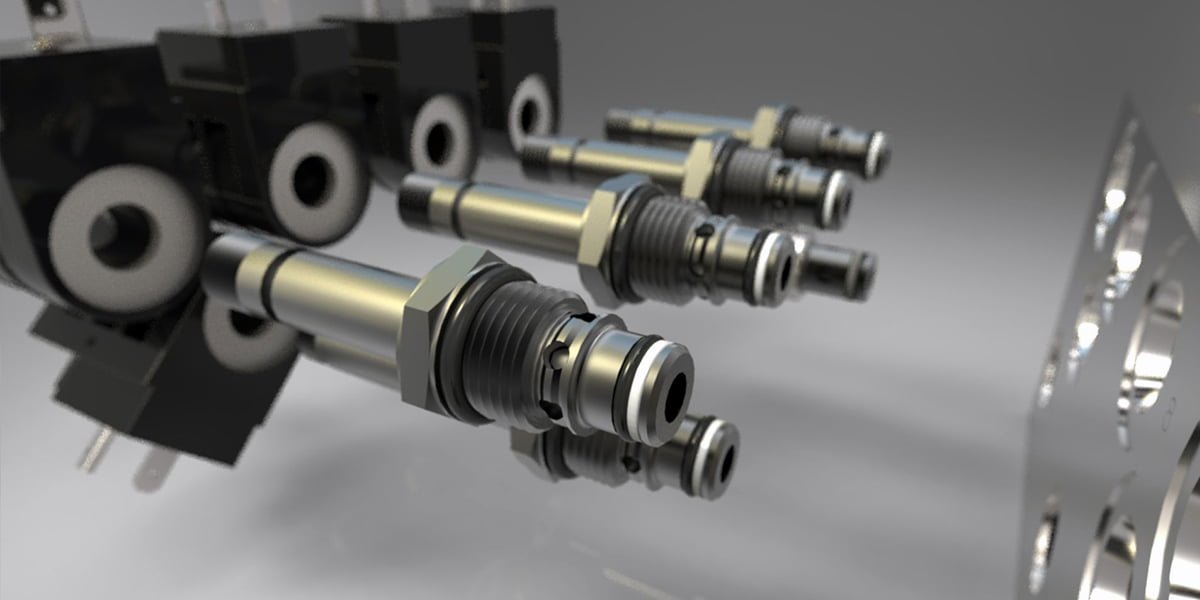

What are the types of solenoid valves?
There are several types of solenoid valves, including:
Direct-acting solenoid valves:
In this solenoid valve type, the plunger directly opens or closes the valve. These valves do not require a differential pressure to operate and are used in low-pressure applications.
Pilot-operated solenoid valves:
In this type of solenoid valve, the plunger controls a small valve that regulates fluid or gas flow through the main valve. These valves use a pilot valve to control fluid or gas flow and are used in high-pressure applications.
2-way selenoid valves:
These valves have two ports, an inlet, and an outlet, and are used to open or close fluid or gas flow.
3-way selenoid valves:
These valves have three ports, two inlet ports, and one outlet port. They are used to divert the flow of fluid or gas between the two inlet ports.
4-way selenoid valves:
These valves have four ports, two inlet ports, and two outlet ports. These valves control the direction of fluid or gas flow. They can be used for applications such as hydraulic or pneumatic control systems.
Latching solenoid valves:
These solenoid valves have a magnetic latching mechanism that keeps the valve open or closed without needing a continuous power supply.
High-pressure solenoid valves:
These types of solenoid valves are designed to handle high-pressure fluids or gases and are commonly used in applications such as hydraulic systems or gas pipelines.
How many types of solenoids are there?
There are two main types of solenoids: linear and rotary solenoids. Linear solenoids have a linear motion and are used in applications requiring a straight-line motion, such as solenoid valves. Rotary solenoids have a rotary motion and are used in applications requiring a rotating motion, such as motors.

How to control solenoid valves?
Solenoid valves can be controlled in several ways:
Manual control:
Some solenoid valves have a manual override feature that allows the valve to be opened or closed manually, even when power is not supplied.
Hydraulic control:
Solenoid valves can also be controlled by a hydraulic signal generated by a hydraulic pump.
Electrical control:
Solenoid valves can be controlled by supplying an electrical current to the coil. The magnetic field is generated when the current is supplied and the valve opens or closes.
Pneumatic control:
Solenoid valves can also be controlled by a pneumatic signal generated by an air compressor or a compressed air tank.
Pressure control:
Some solenoid valves can be controlled by adjusting the pressure of the fluid or gas flowing through the valve.
Temperature control:
Some solenoid valves can be controlled by adjusting the temperature of the fluid or gas flowing through the valve.
Remote control:
Solenoid valves can be controlled remotely using a computer or a control system. This system allows the valve to be operated remotely, making it suitable for automation applications.
Conclusion On Solenoid Valves
Solenoid valves are versatile electromechanical devices that are widely used in various industries. They are essential components in a wide range of industrial applications. They are reliable, durable, and can be operated remotely, making them an ideal choice for many applications.
In this post, we discussed solenoid valves, their uses, functions, working principle, types, and how to control them. By understanding the types and functions of solenoid valves and how to control them, you can select the right solenoid valve for your application and ensure reliable, efficient, and safe operation.